MEF’s (of which iTouch is a member) recently published Enterprise Mobile Messaging Fraud Framework 2.0, developed by MEF’s cross-sector Working Group and part of the Future of Messaging Programme, identifies the 13 types of fraud that are affecting the messaging ecosystem and the measures needed to tackle these sharp practices.
Messaging fraud education
We have already covered what SMS originator spoofing is in our previous post and this week we will be taking you through another popular technique of defrauding clients using messaging, known as SMS phishing.
For the latest on the fraud frame work check out our article The Global Fraud Messaging Guide Updated For 2017
What exactly is SMS phishing?
SMS Phishing, also known as SMiShing, is a form of criminal activity combining Spam, SMS Originator Spoofing and social engineering techniques to pretend to be a trustworthy entity, in order to gain access to online systems, accounts or data such as credit card, banking information or passwords, for malicious reasons.
Diagram of how SMS phishing works
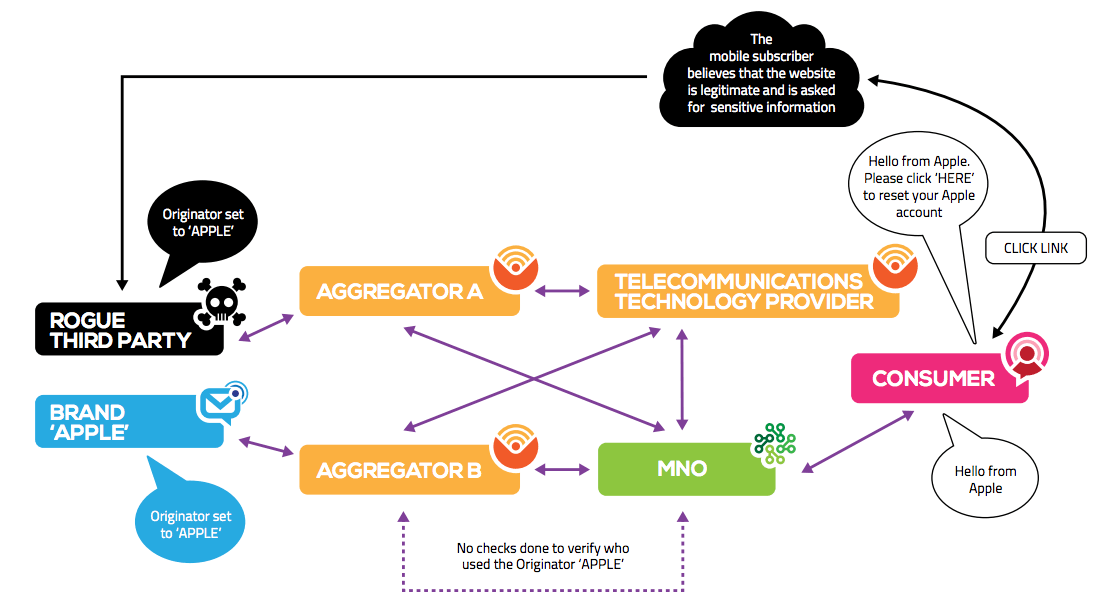
The cause of SMS phishing
- The promise of financial gain, either directly or indirectly through data loss
- Increasing incidence in line with the growth of smartphone adoption and reliance of mobile applications
- The ease with which consumers can be fooled through the use of basic social engineering and masquerading techniques to engender trust – consumers respond automatically to familiar situations and messages and may not be aware of or looking for potential risks
- Senders can use a percentage-based approach and so do not need to know whether a consumer has a relationship with the enterprise they are pretending to be, although having that information will increase their likelihood of success
- An enterprise not effectively managing their relationship with their customer, including proactively reiterating what channels they use to communicate with their customers and stating explicitly what information they will not ask for under any circumstances
- Poor regulation of the providers of enterprise mobile messaging solutions
Other contributing factors to the growth of SMS phishing
- Other contributing causes include : Use of Two Factor Authentication (2FA) codes creates a perceived layer of trust
- Network support for “dynamic” alpha originators
- Number harvesting tools which gather MSISDNs and associated personal information
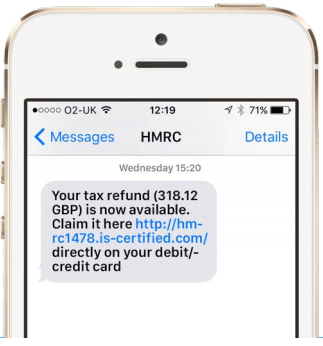
Example of SMS phishing
Contact us
If you're company is a victim of SMS spoofing and would like to know more about how to prevent spoofing or you're looking for a trusted bulk SMS service provider then contact us here.
